Integumentary System Of A Fish
Integumentary system of a fish. This allows them to consume larger prey. The two layers differ in. Their digestive system is complete and includes several organs and glands.
The food goes into the mouth chew up by the teeth saliva made by saliva glands andor tongue. In animals it serves to waterproof cushion and protect the deeper tissues excrete. The integumentary system is primarily the skin but includes things that grow out of it like hair fur finger and toe nails hooves if youre a quadruped scales if youre a fish and feathers if youre a bird.
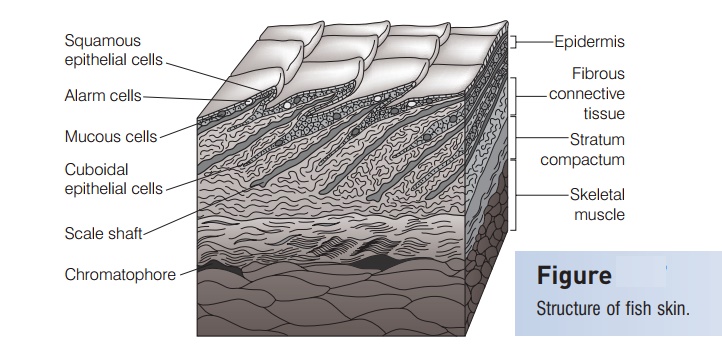
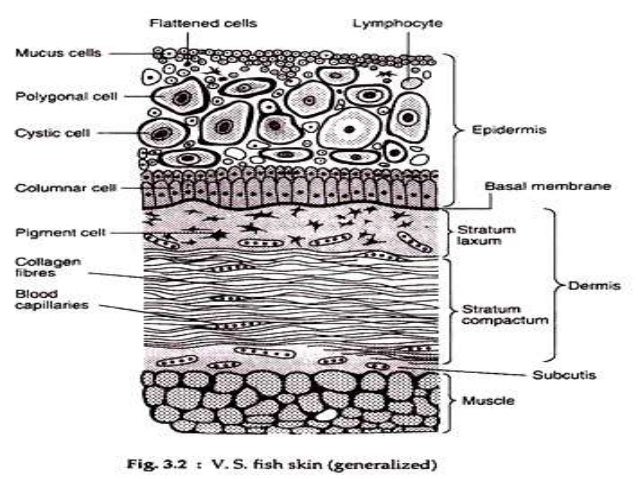
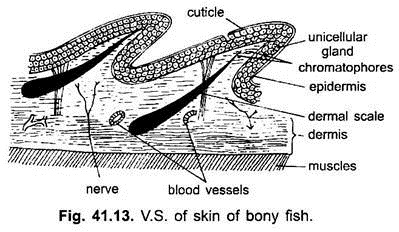
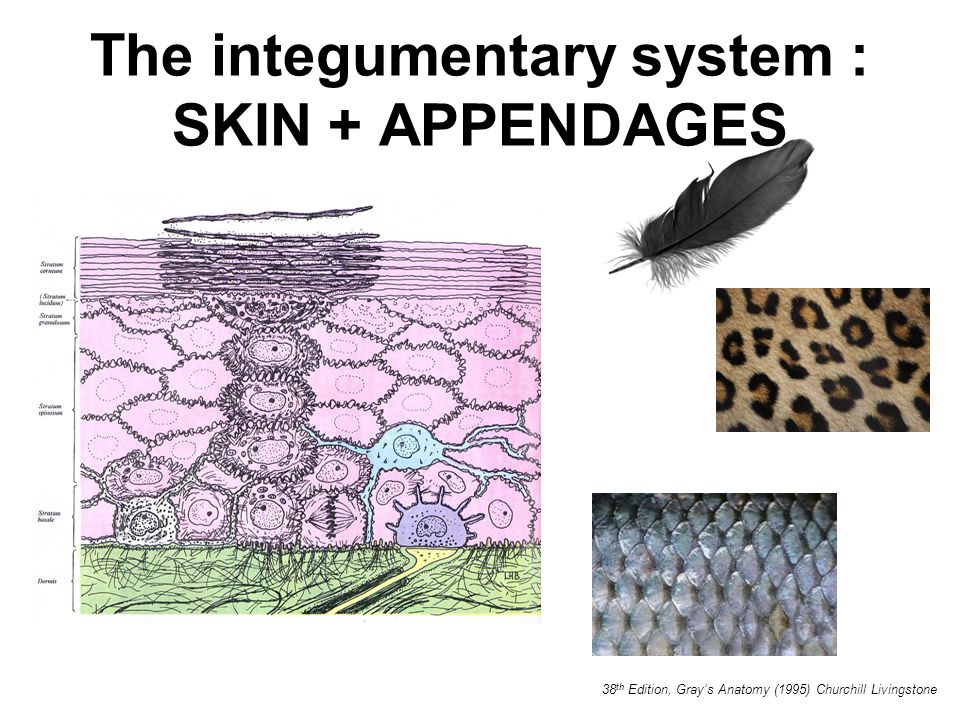
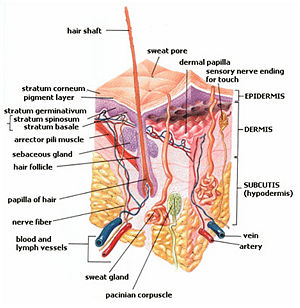
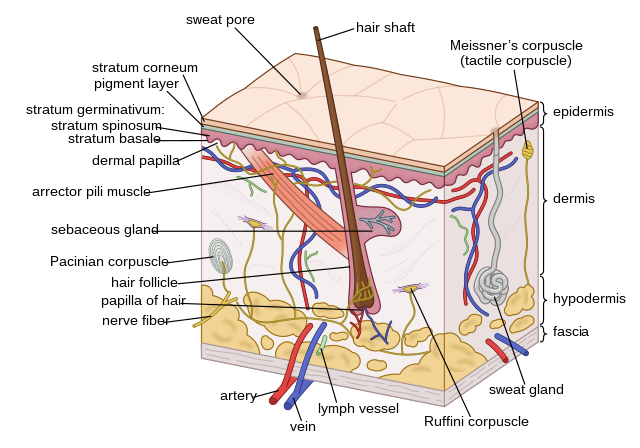
The integumentary system includes hair scales feathers hooves and nails. It protects the body from external injury parasites fungus bacteria and other microorganisms. Fish integument is a large organ that is continuous with the lining of all the body openings and also covers the fins.
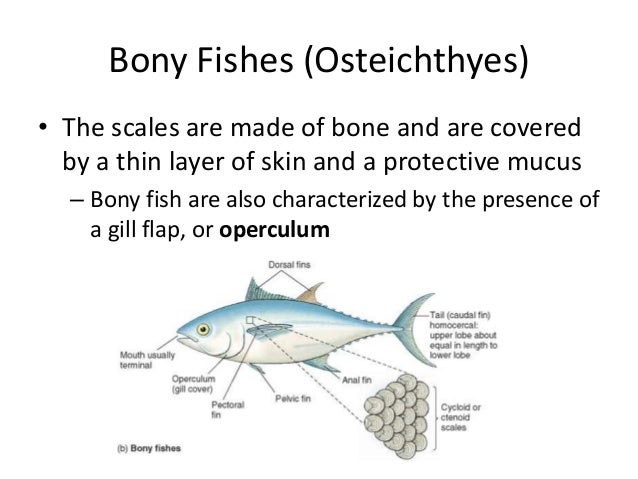
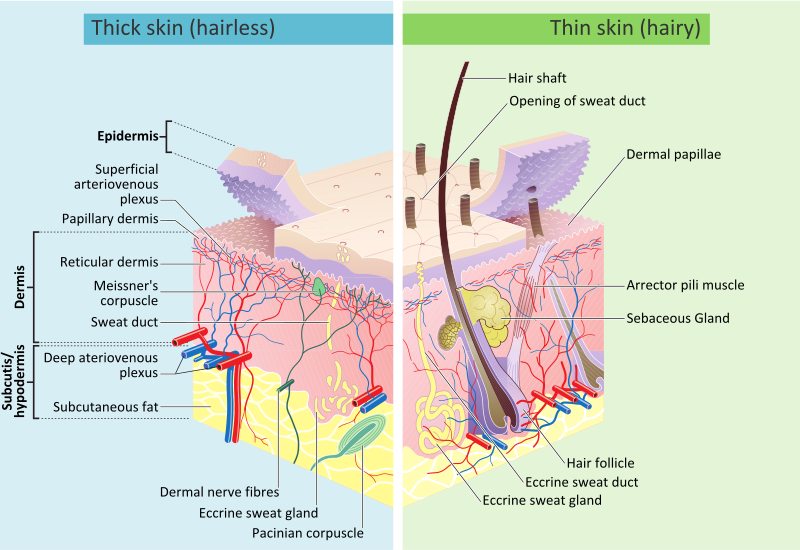
The integumentary covering of the feet the podotheca is a layer of scales from the tibiotarsus or beyond to the ends of the toes. Among the cartilaginous fishes sharks have a very tough skin. Generally mammalian skin is thicker than the skin of other vertebrates because of its function in retarding heat and water loss.
These structures grow out of and are continuous with the epidermis and consist of hair follicles sebaceous and sweat glands and specialized structures eg claw hoof. It comprises the skin and its appendages acting as a physical barrier between the external environment and the internal environment that it serves to protect and maintain. The integumentary system is the set of organs forming the outermost layer of an animals body.
In some species eg. The integumentary system consists of the skin the feathers and the appendages claws and beak. Anatomy of Snails gastropoda Integumentary System Daniel Takacs Respiratory System Shell AQUATIC SNAILS Shells of a land snail can be many different sizes depending on species Shells are used as protection against.
Fish have a circulatory system with a two-chambered heart. The digestive system begins with the mouth and teeth which trap food and help send it on to the stomach and intestine for digestion.
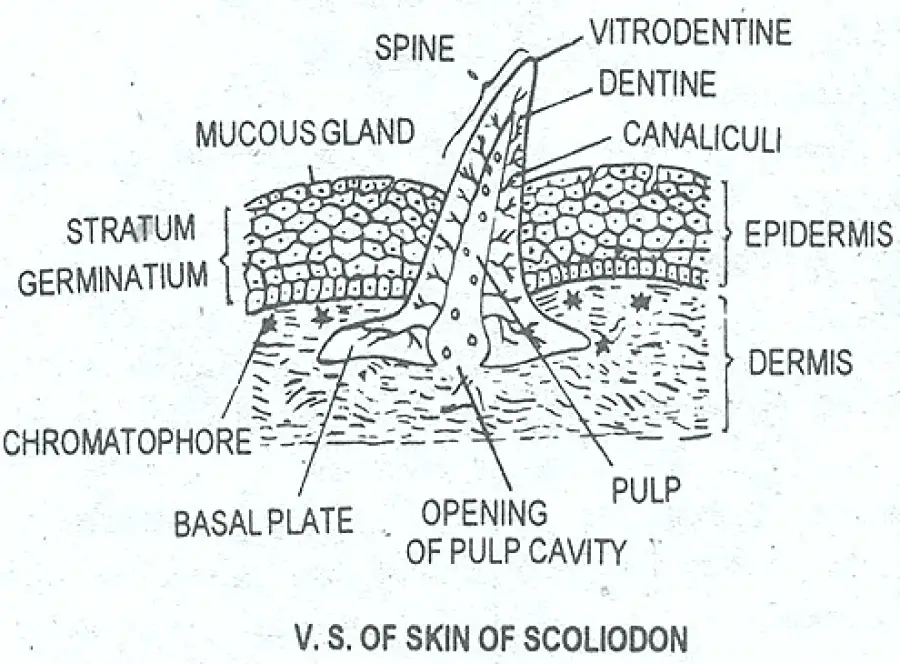
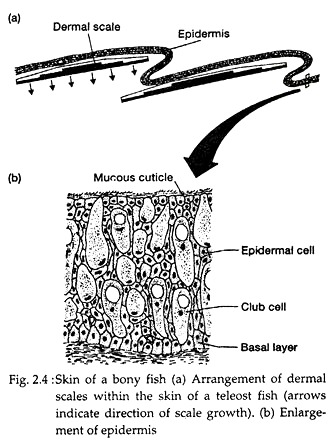
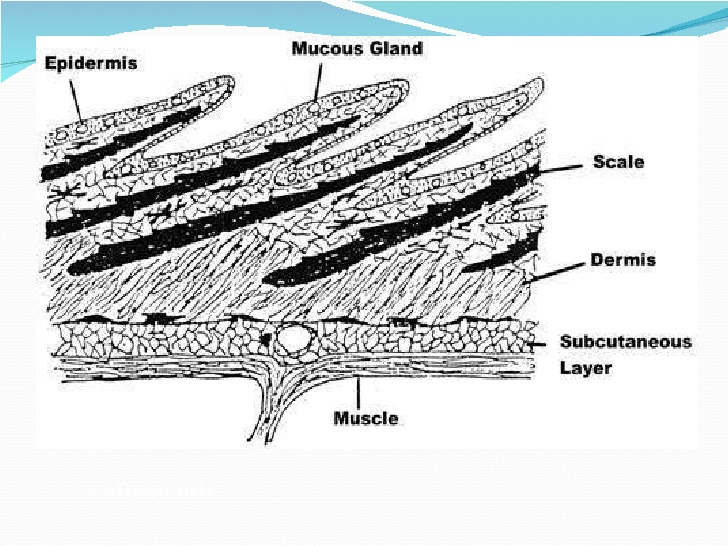
These cells secrete the dentine or calcareous material of the scale.
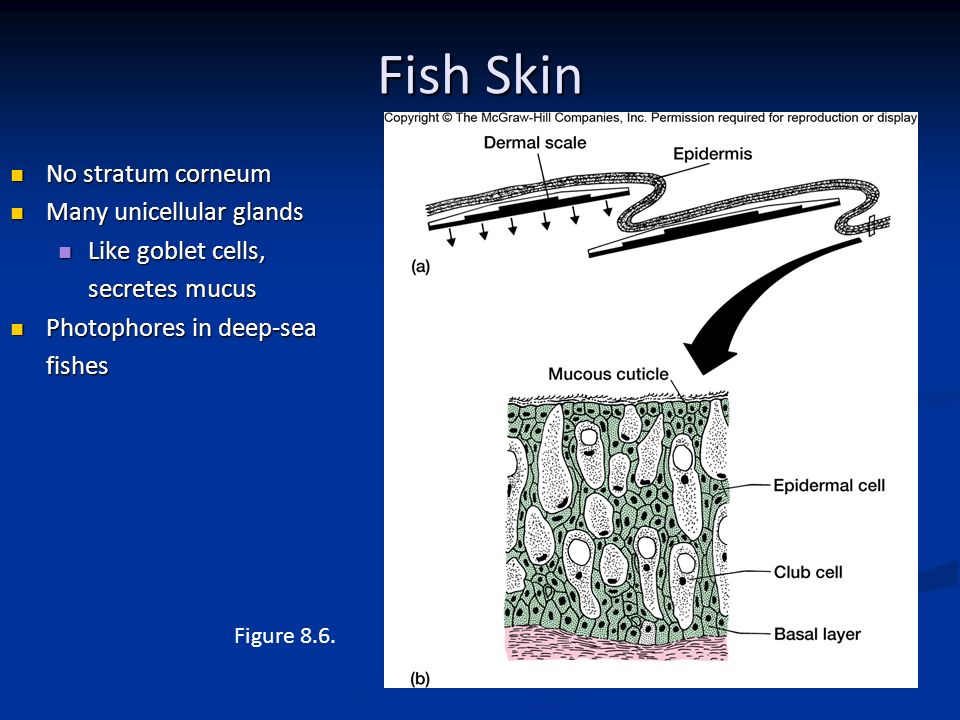
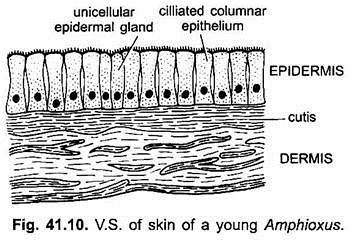
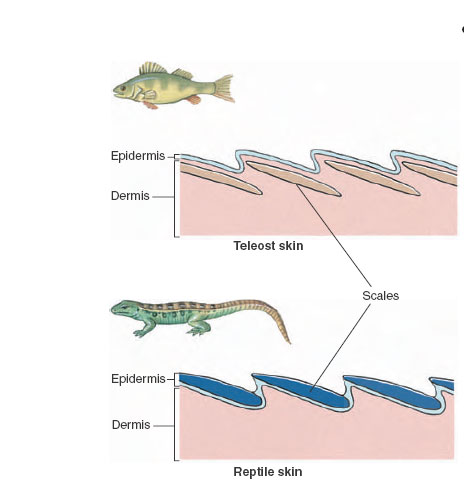
The structure of the skin in fishes is similar to that of other vertebrates with two main layersan outer epidermis and an inner dermis. Generally mammalian skin is thicker than the skin of other vertebrates because of its function in retarding heat and water loss. In animals it serves to waterproof cushion and protect the deeper tissues excrete. An outer epidermis and an inner dermis or corium. The mammalian integument has many of the characteristics that we consider mammalian. In addition to its protective functions fish skin may serve important roles. Integumentary system - Wikipedia. These cells secrete the dentine or calcareous material of the scale. The integumentary system is composed of the skin and its accessory organs.
The food goes into the mouth chew up by the teeth saliva made by saliva glands andor tongue. The integument is continuous with the lining of all the body openings and also covers the fins. The integumentary system is an organ system that forms the protective covering of an animal and comprises the skin including glands and their products haircoat or feathers scales nails hooves and horns. The forebrain of fish is dominated by the olfactory lobes see fish olfactory system which extend forwards and may be placed at the end of stalks. Fish Organ Systems. The skin is the envelope that provides both communication with the environment as well as protection against adverse external agents or mechanical damage with a high capacity for. The structure of the skin in fishes is similar to that of other vertebrates with two main layersan outer epidermis and an inner dermis.




























:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/a-Anatomy-of-an-aquarium-fish-5-5802eafe3df78cbc28867d3d.jpg)
Post a Comment for "Integumentary System Of A Fish"