Non Oxidative Energy System
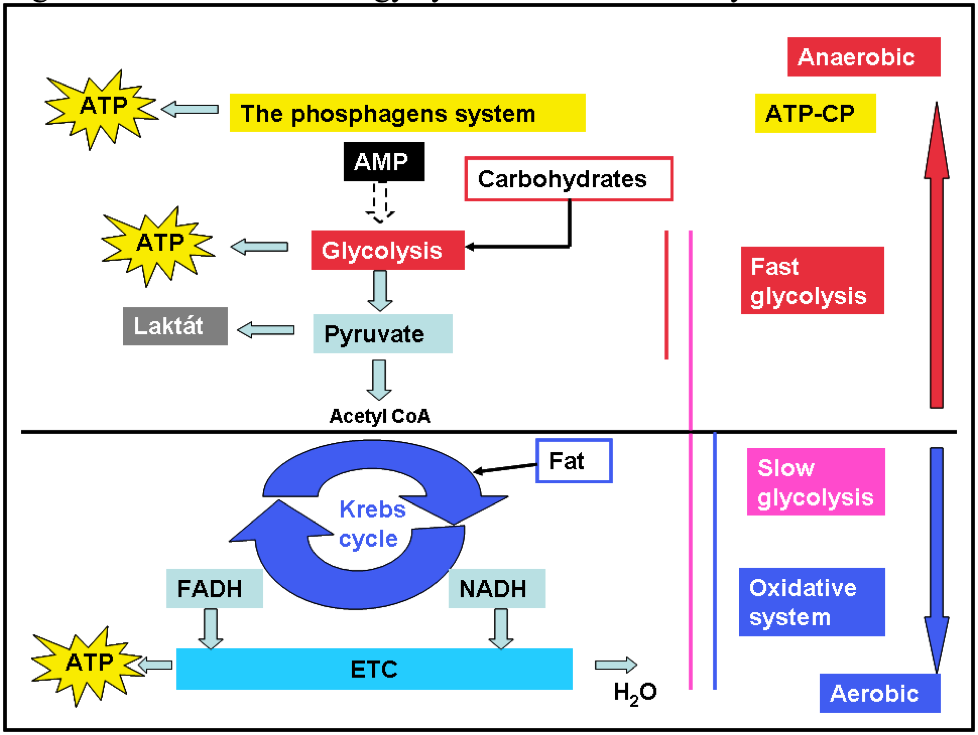
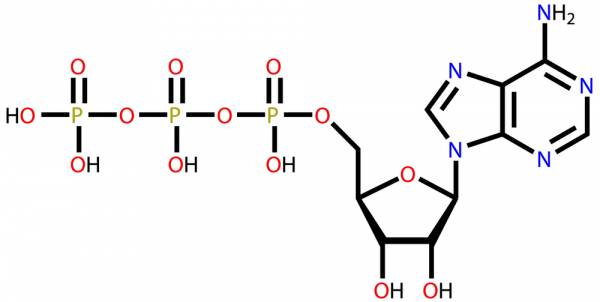
Non oxidative energy system. The Immediate Energy System. The Immediate Energy System in skeletal muscle utilizes several integrated chemical reactions to liberate energy for cellular work in an explosive rapid sequence but then quickly put the ATP back together again. Protein is typically not utilized during this energy system except during bouts of exercise greater than ninety minutes and during starvation.
Down up efforts Starting on stomach up run forward 5m down flat to stomach up as quickly as possible running backwards 5m. Oxidative stress a condition in which the effects of pro-oxidants eg free radicals reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen species exceed the ability of antioxidant systems to neutralize them. 1 This means it is critical to be taking in enough calories of carbohydrates and fats to fuel endurance activity.
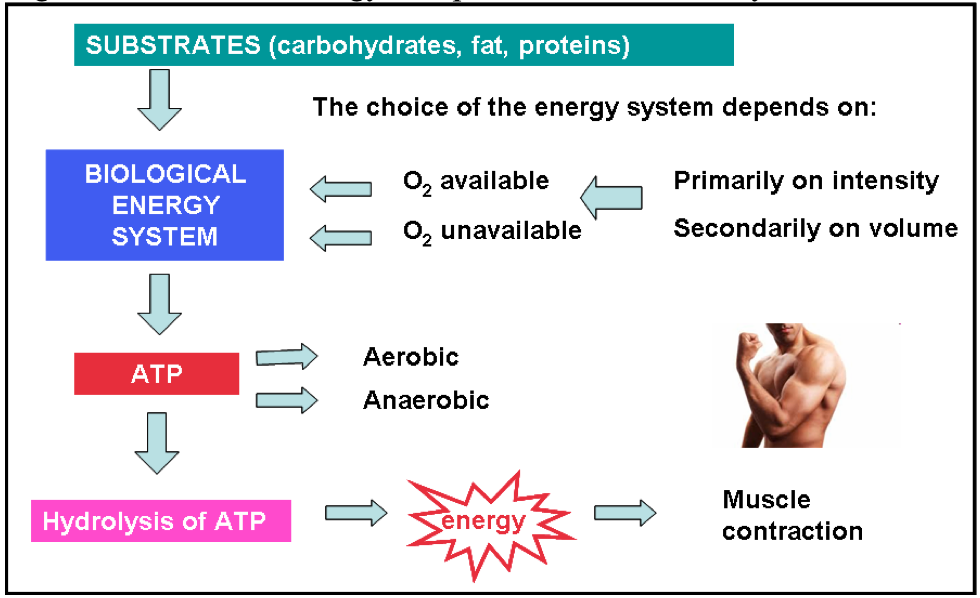
These systems are usually discussed in isolation but the reality is they overlap and are all working at the same time. Fats and carbs are the primary substrates that are used. The three energy systems work together to supply your bodys energy needs.
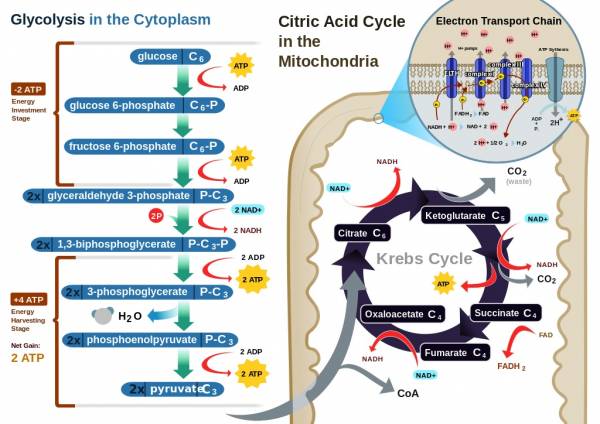
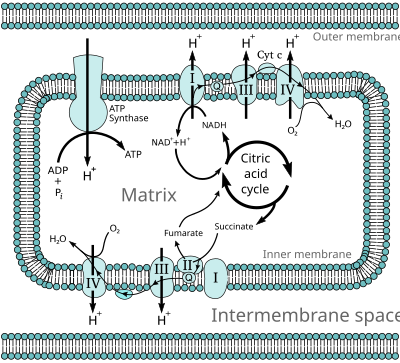
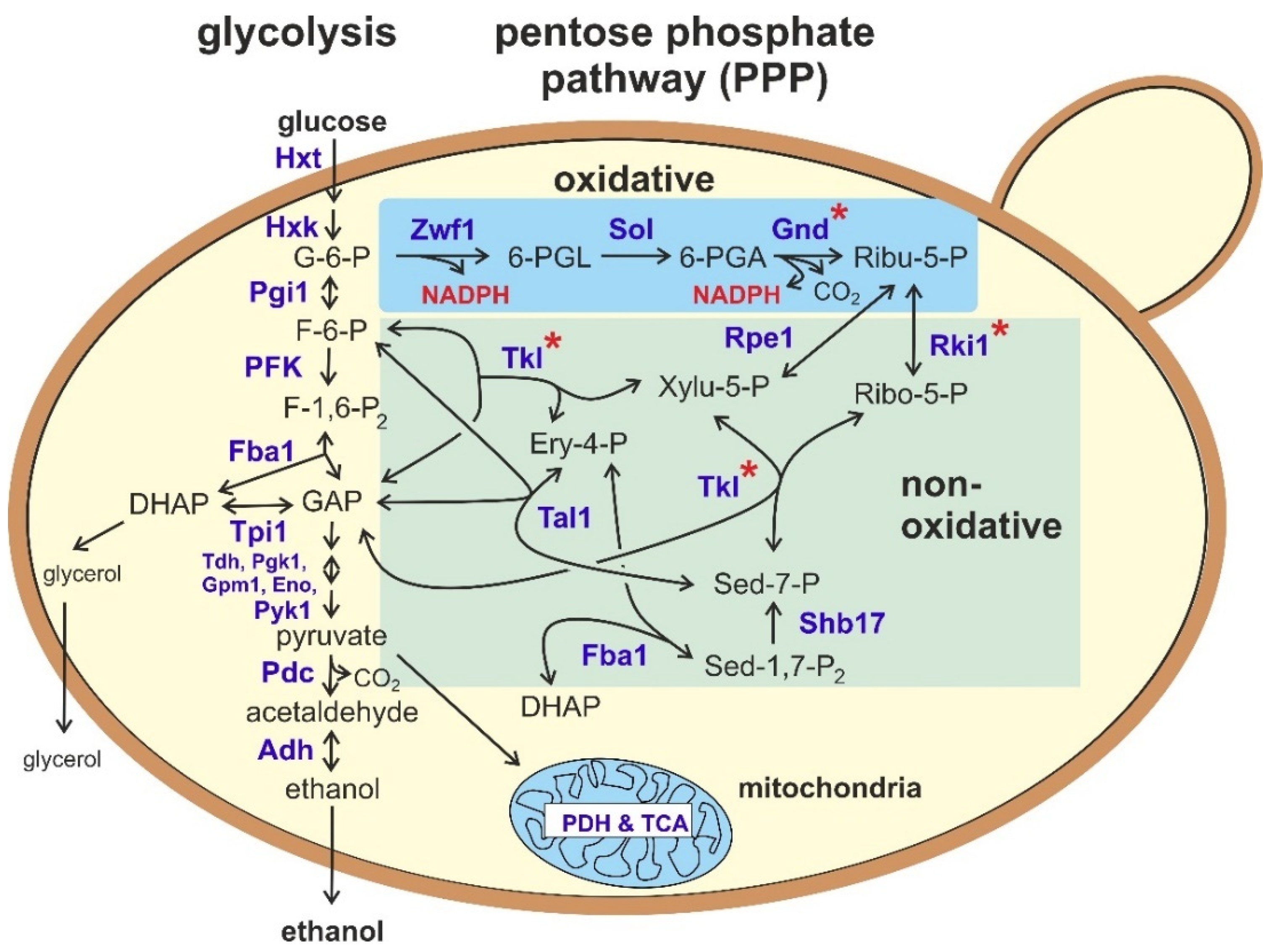
The non-oxidative energy system could provide energy for up to. In this system carbohydrates and fats are the primary energy sources converted into ATP and this process takes place in the mitochondria of the cell. The initial step is removal of two hydrogen atoms by the flavin coenzyme with formation of an unstable α-amino acid intermediate.
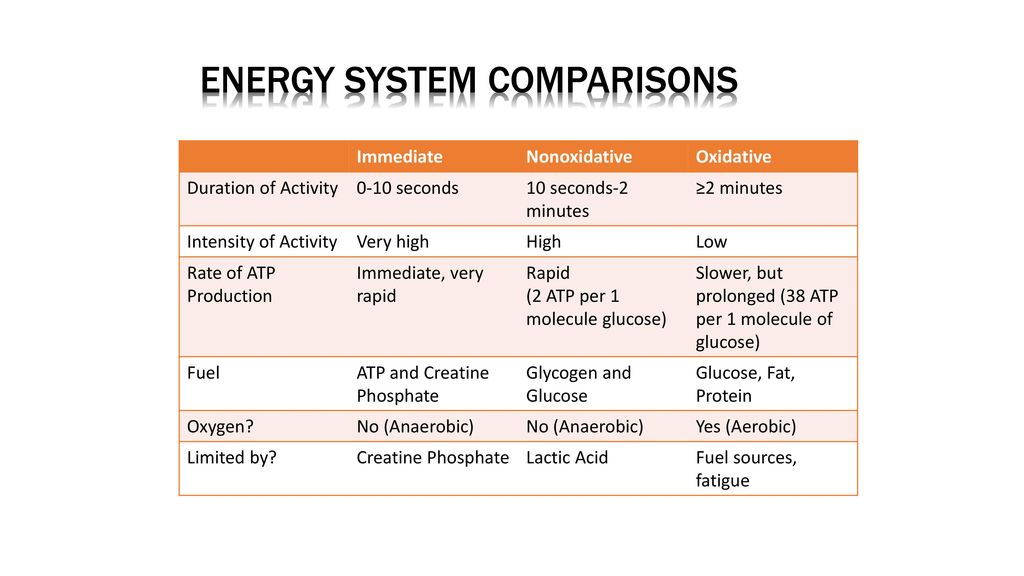
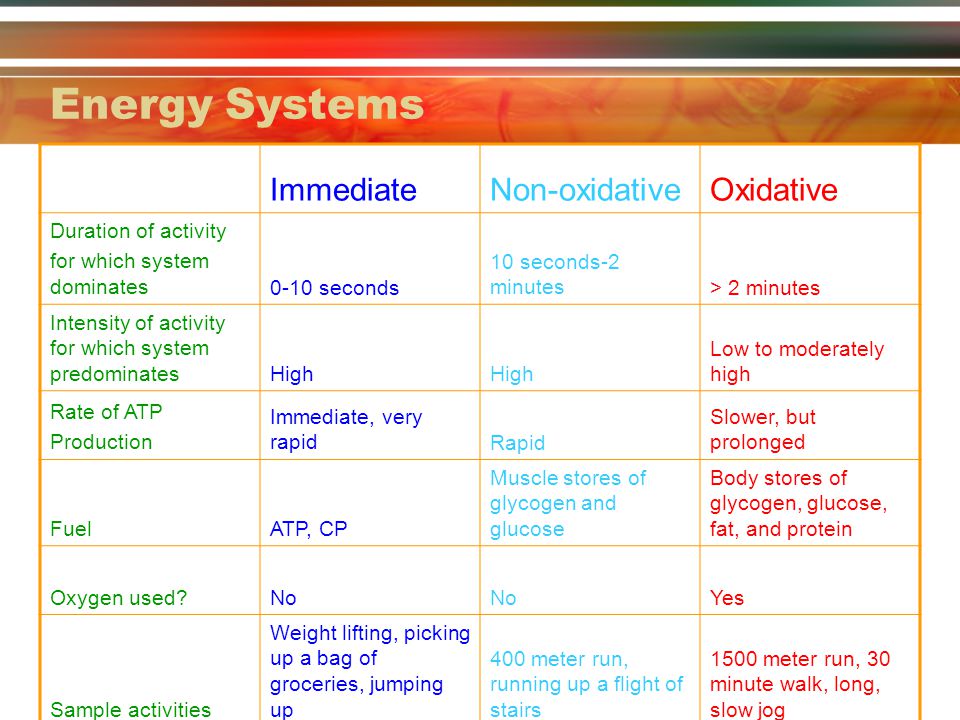
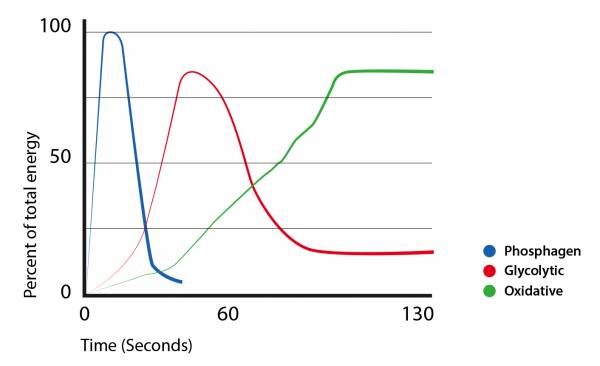
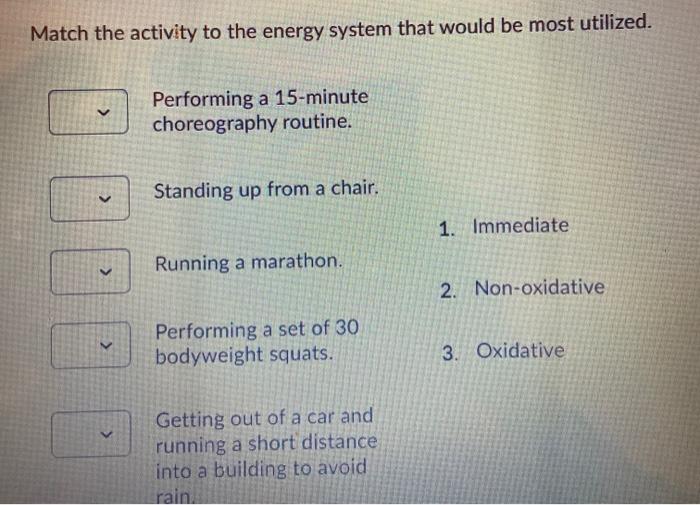
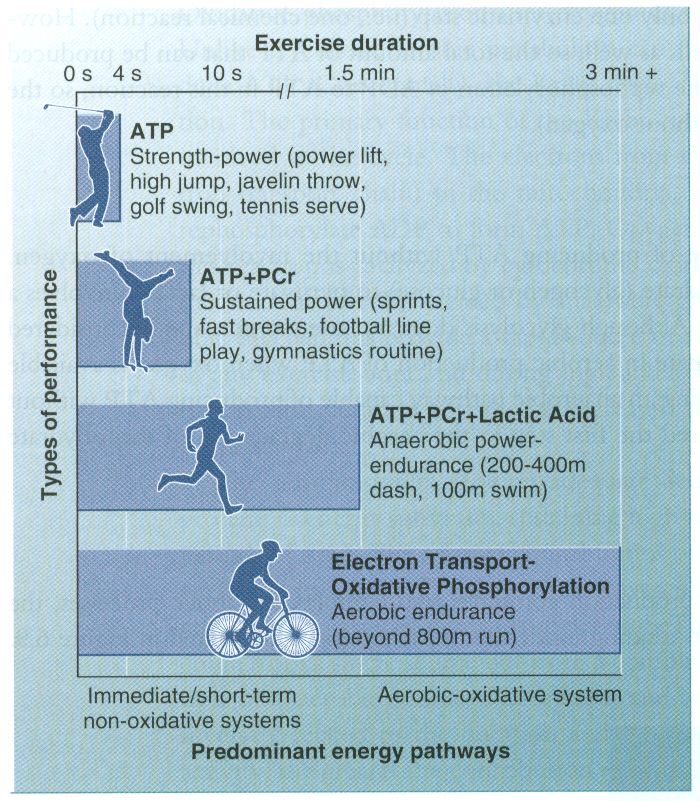
Sport Basketball ATP-PC 60 Anaerobic Glycolytic 20 Aerobic 20. Lasts for 10-120 seconds. Introduction The oxidative system consists of four processes to produce ATP.
Its just that depending on how quickly energy is required one system will be more dominant than the others. The capacity to generate power of each of the three energy systems can vary with training. However its not as simple as the body just switching energy systems like a car switches gear.
There the removed amine group converts into ammonia and excreted from our body. As long as needed d.
The capacity to generate power of each of the three energy systems can vary with training.
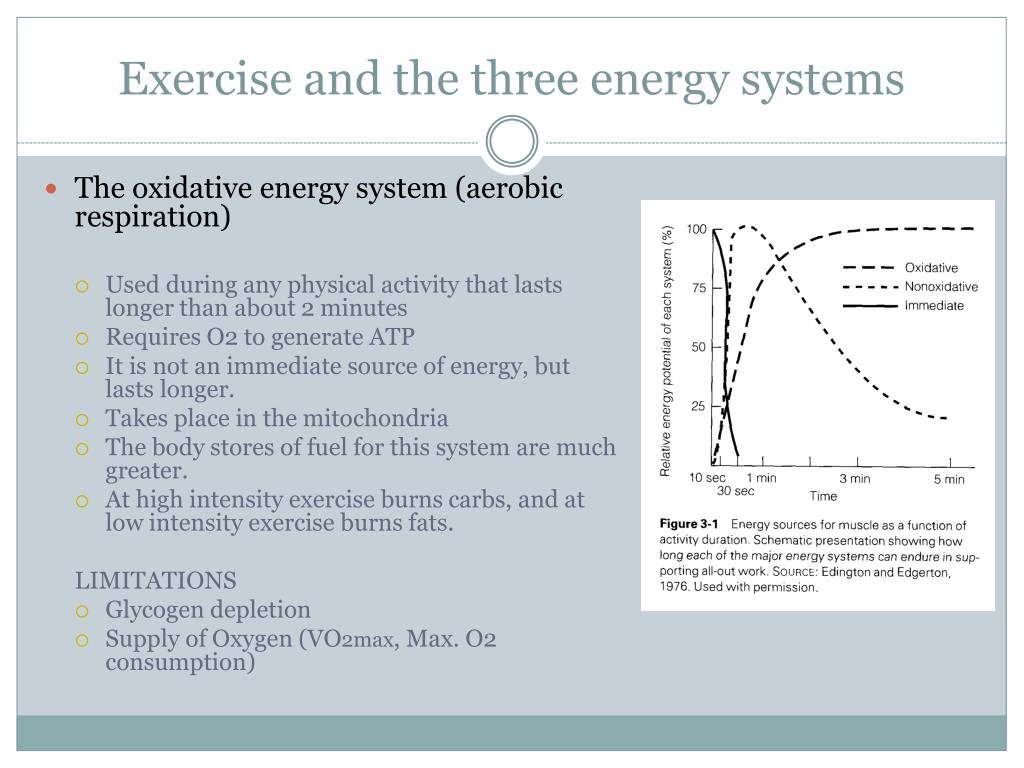
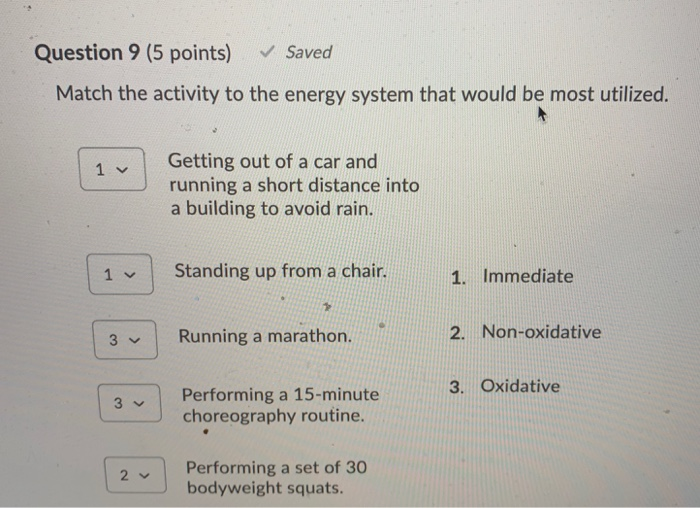
The capacity to generate power of each of the three energy systems can vary with training. Instead the cells where the ATP is produced require glucosecarbohydrates that have been broken down as the fuel source. The anaerobic glycolysis energy system produces energy by partially breaking down Glucose anaerobically no oxygen. Now one thing I dont understand from your answer is how can the body use glucose. As the name implies the non-oxidative energy system does not require oxygen to generate ATP. Up to 2 minutes c. The three energy systems work together to supply your bodys energy needs. The body can actually use multiple energy systems but always is using one predominately. Creates atp by breaking down glucose and glycogen.
Like the immediate energy system this system is associated with high intensity and short duration movements. Up to 5 minutes. The oxidative energy system is the primary source of ATP at rest and during low intensity exercise. Like the immediate energy system this system is associated with high intensity and short duration movements. A major consequence of oxidativenitrosative stress is. However its not as simple as the body just switching energy systems like a car switches gear. The Immediate Energy System in skeletal muscle utilizes several integrated chemical reactions to liberate energy for cellular work in an explosive rapid sequence but then quickly put the ATP back together again.


























Post a Comment for "Non Oxidative Energy System"